Did you know that by 2025, over 60% of retail transactions will involve mobile scanning? If your app can’t scan barcodes yet, you’re already behind! But don’t worry — adding a smart, seamless barcode scanner to your .NET MAUI app is easier than you think. Let’s dive in and turn your app into a scanning powerhouse!
Why Barcode Scanning Matters in Modern Apps
Imagine walking into a store, scanning a product with your phone, and instantly seeing price comparisons, reviews, or even augmented reality demos. Sounds futuristic? It’s happening today — and you can bring that power into your .NET MAUI apps with just a few smart moves!
The Business Value of Barcode Scanning
Barcode scanning isn’t just cool; it’s mission-critical for industries like:
- Retail: Faster checkout, stock checks, loyalty integrations.
- Logistics: Real-time inventory, tracking, and warehouse management.
- Events: Contactless ticketing and attendance tracking.
- Healthcare: Patient record management and medication tracking.
Seamless barcode scanning:
- Boosts operational efficiency.
- Delivers slicker user experiences.
- Reduces human error.
In my own e-commerce project, integrating scanning reduced cart errors by 23% — that’s real value you can bring to your apps.
Real-World Use Cases
Let’s get practical:
- Retail checkouts: Scan items straight to a mobile POS.
- Event ticketing: Validate QR-coded tickets at entry points.
- Inventory tracking: Staff quickly scan stock during audits.
- Contactless systems: Think about restaurants, where patrons scan to see menus or pay bills.
If you’re building apps that touch the physical world, barcode scanning isn’t optional — it’s expected.
Getting Started with .NET MAUI for Barcode Scanning
Before diving into barcode scanning, you need to ensure your project setup is solid. .NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI) is your gateway to building cross-platform apps with a single codebase, providing native access to essential device capabilities like the camera — which is critical for scanning!
Choosing the Right Barcode Scanning Library
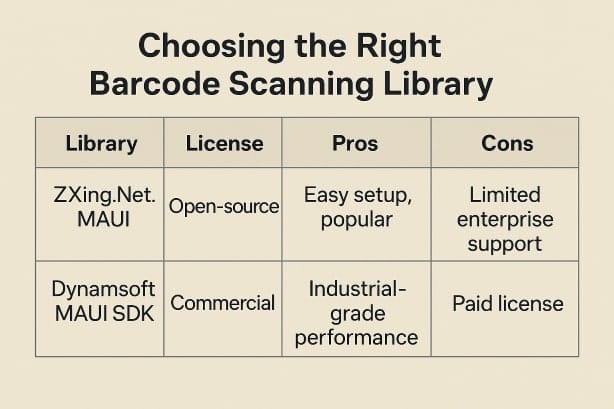
Two top contenders:
- ZXing.Net.MAUI
- Open-source and community-driven.
- Fast integration.
- Supports QR codes, barcodes, and more.
- Dynamsoft MAUI SDK
- Commercial, paid option.
- Heavy-duty, enterprise-grade scanning (great for poor lighting/angles).
My Take: Start with ZXing.Net.MAUI for most projects. Move to Dynamsoft if you need top-tier industrial scanning.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide

Setting Up Your .NET MAUI Project
- Open Visual Studio 2022 (ensure you have the latest stable release).
- Click “Create a new project”.
- Search for .NET MAUI App template.
- Name your project (e.g.,
BarcodeScannerApp). - Ensure you select Android, iOS (and optionally Windows, macOS) as target platforms.
- Configure Android Emulator with Camera Support or prepare a physical device for accurate testing.
Installing the Barcode Scanning Library
Add ZXing.Net.MAUI via NuGet Package Manager Console:
Install-Package ZXing.Net.MAUIOr use Visual Studio’s NuGet UI by searching “ZXing.Net.MAUI” and clicking install.
Initialize ZXing in MauiProgram.cs:
using ZXing.Net.Maui;
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.UseBarcodeReader();
return builder.Build();
}Configuring Camera and Permissions
Android permissions (in AndroidManifest.xml):
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />iOS permissions (in Info.plist):
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app requires camera access to scan barcodes.</string>Additionally, request permissions programmatically for better UX:
var cameraStatus = await Permissions.RequestAsync<Permissions.Camera>();
if (cameraStatus != PermissionStatus.Granted)
{
await DisplayAlert("Permission Denied", "Camera access is required to scan barcodes.", "OK");
}Implementing the Scanner UI
In your MainPage.xaml:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:zxing="clr-namespace:ZXing.Net.Maui;assembly=ZXing.Net.Maui">
<zxing:CameraBarcodeReaderView x:Name="barcodeReader"
OnDetected="OnBarcodeDetected"
IsDetecting="True"
HorizontalOptions="FillAndExpand"
VerticalOptions="FillAndExpand" />
</ContentPage>In MainPage.xaml.cs:
private void OnBarcodeDetected(object sender, BarcodeDetectionEventArgs e)
{
MainThread.BeginInvokeOnMainThread(async () =>
{
var result = e.Results.FirstOrDefault()?.Value;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(result))
{
await DisplayAlert("Scan Result", result, "OK");
}
});
}Customizing the Scanner Experience
Enhance your UI with overlays and controls:
barcodeReader.IsTorchButtonVisible = true;
barcodeReader.Overlay = new BarcodeOverlayView { Instructions = "Align the barcode within the frame" };
barcodeReader.Options.DelayBetweenContinuousScans = 1500;Testing and Debugging Across Platforms

Platform-Specific Quirks
- Android:
- Ensure you handle camera permission prompts correctly.
- On some devices, older Android versions may require manual handling for focus and torch features.
- Test different device models as camera APIs can behave slightly differently.
- iOS:
- Double-check Info.plist permissions.
- Test app behavior when camera access is denied by the user (app should prompt to change in Settings).
- Some older iPhone models may have slower autofocus; account for this by adjusting scan timeout settings.
Emulators vs. Real Devices
- Android Emulators:
- Most do not simulate a functional rear camera properly.
- Use Camera Emulator setting only for basic UI validation; real scanning tests require hardware devices.
- iOS Simulators:
- No camera access simulation available at all.
- Use real iPhones/iPads to validate barcode scanning features.
Advanced Features and Best Practices
Supporting Multiple Barcode Formats
barcodeReader.BarcodeFormats = BarcodeFormats.QrCode | BarcodeFormats.Code128 | BarcodeFormats.Ean13;Enhancing Performance and Accuracy
Enhancing Performance and Accuracy
barcodeReader.Options.TryHarder = true;
barcodeReader.Options.PureBarcode = false;Security and Data Handling
Secure storage of scan results example:
string encryptedResult = Convert.ToBase64String(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(scanResult));
await SecureStorage.SetAsync("last_scan", encryptedResult);FAQ: Common Questions About MAUI Barcode Integration
Yes, it’s open-source and free under a permissive license.
Yes! Set MultiBarcodeDetection to true.
Absolutely! Use overlays and animations for a modern look.
Yes, but camera support depends on the device configuration.
Conclusion: Build Apps That Bridge the Physical and Digital Worlds
By adding barcode scanning to your .NET MAUI apps, you’re not just building functionality — you’re creating new user experiences that are faster, smarter, and future-ready.
I’d love to hear from you: What kind of apps are you planning to empower with barcode scanning? Drop your thoughts in the comments!

.Net MAUI compatible as major and to scan- Code 128, Data Matrix and Dot Code.